| Bookmark Name | Actions |
|---|
Overview
This section helps you to learn about the Scheduler features, design, internal working procedure and payloads.
Features
In Microservices Framework (MSF), Scheduler provides the following features:
- Allows configuration of multiple schedulers
- Supports tracking or monitoring of scheduler instances at any point of time
- Provides configuration for supplying parameters at runtime
- Provides support for adding pre-hook and post-hook operations
- Available and tested in all framework supported environments (that is Docker, J2EE, AWS, Azure)
- Easy to implement and use
Design
Scheduler feature is designed based on the command-event flow in MSF. It reuses the existing command-event flow model to facilitate monitoring the status of scheduler instances at any point of time.
Below is an overview of the scheduler features execution or flow in Temenos Microservices Framework.
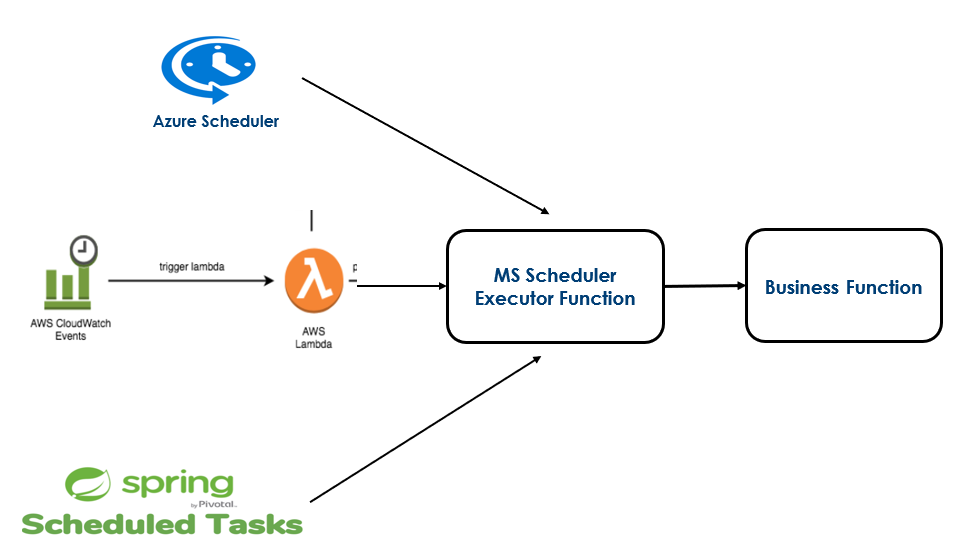
Internal Working
Scheduler execution takes place as per the following steps:
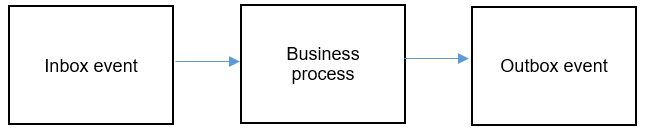
- When a scheduler is triggered, an inbox event (command event) is raised and an entry is created in ms_inbox_events table. The entries in ms_inbox_events table contains information about the event triggered such as eventType, commandType, payload, status, etc.
- It is then followed by business process execution that is implementation in underlying microservice.
- Once the business process execution completes, irrespective of success or failure, an outbox event (command event) is raised and an entry is created in the ms_outbox_events table. The entries in ms_outbox_events contains information about the triggered event such as eventType, commandType, payload, status, etc.
A flow diagram depicting the internal working of a scheduler executor is as follows:
The events raised as part of scheduler execution have the following properties:
- "commandType": "SCHEDULER"
- "eventType": <MSname>.<operationId>
Payloads
This section shows the input and output payload.
SchedulerExecutor class acts as the entry point for a scheduler. The input object that is SchedulerCommandInput required for scheduler execution has following attributes. The input object attribute values are passed as properties or environment variables.
| Attribute name | Datatype |
|---|---|
|
operationId* |
String |
|
parameters |
Map<String,String> |
Where, * indicates mandatory attribute name.
For attribute parameters, certain keywords, if passed as keys with appropriate values are added to command event object for processing. If not provided, then default, auto-generated or null values will be used. The keywords include:
- eventId
- organizationId
- tenantId
- userId
However, the mode of ingestion of inputs into the scheduler executor varies with environment that is JSON file in docker, environment properties in AWS or Azure. The payload in input object can be verified from ms_inbox_events table.
The response object that is SchedulerCommandOutput has following attributes.
| Attribute name | Datatype |
|---|---|
|
operationId |
String |
|
message |
String |
|
data |
Map<String,Object> |
The output or response object is added as body of business object in payload. The same can be verified from ms_outbox_events table.
For reference, see a sample inbox and outbox event object containing payloads.
Add Bookmark
save your best linksView Bookmarks
Visit your best links BACK
BACKIn this topic
Are you sure you want to log-off?



