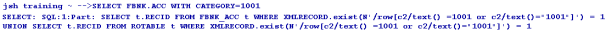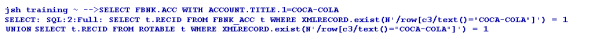| Bookmark Name | Actions |
|---|
MSSQL
The Temenos Transact Microsoft SQL Server Direct Connect driver is a middleware component between Temenos Transact and MSSQL server database. It enables Temenos Transact to send to and retrieve data from MSSQL server database storage. The data is stored in MSSQL server as either XML columns or BLOBs (Binary Large Objects) for internal or work files. This section provides details about the database configuration, commands, transactions and driver environment variables involved in multiple database access and table details.
Having huge Temenos Transact data in single server or database hinders the performance of the database in both transactional and reporting services. Therefore, this data need to be separated categorically as per the business needs.
The Temenos Transact data is classified into volatile (transactional) and non-volatile (read-only) data. The data is separated and stored in different databases, which:
- Boosts the performance of the transactional processing
- Enables timely retrieval of the historical (non-volatile) data for the reports
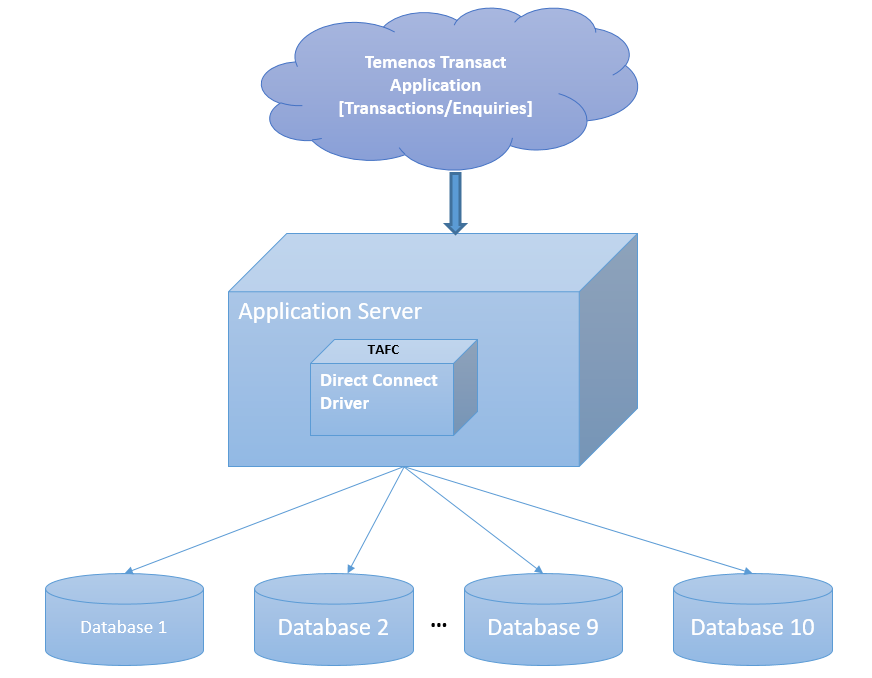
The MS SQL Server Direct Connect Driver (DCD) enables you to configure and access maximum of ten databases. Each database can be configured with its own credentials. A table can be created in a specific database for an easier and accurate access. Each table has two columns as listed in the following table.
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
RECID |
Holds the primary key of the table |
|
XMLRECORD |
Holds the table data |
If the XMLRECORD is of XML type, the data will be converted from the internal dynamic array format into an XML sequence for insertion into the MSSQL server database. If the record is of BLOB type, the data will be stored directly in the XMLRECORD column in binary format.
On retrieval of data, the row information from the XMLRECORD column is converted back from an XML sequence into the internal dynamic array format for use by the application.
Database Configuration
You can get the MSSQL server home path and add the following in remote.cmd.
- SET SQL_HOME=C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server\100\Tools
- SET PATH=%PATH%;%SQL_HOME%\Binn
To access the database, you need to use the MSSQL command line tool sqlcmd.
You can check the version of MSSQL server in the About option in the drop down from the Help in MSSQL Server Management Studio.
SQL Server 2008’s server authentication must be set to SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode for the Temenos Transact user to access to the database. You can set this either during the initial installation of SQL Server 2008 or at a later stage.
The XMLMSSQLDriver is located in %TAFC_HOME%\XMLMSSQL folder. The following table lists the libraries and executables available in the driver.
|
Libraries |
Executable |
|---|---|
|
config.XMLMSSQL.dll config-XMLMSSQL.dll |
Dynamic linked library for MSSQL server Driver |
|
config.XMLMSSQL.exe config-XMLMSSQL.exe |
Executable used for the MSSQL server driver configuration |
|
libTAFCTransformer.dll |
Dynamic linked library from TAFC. |
|
libTAFCmssqlutils.dll |
Dynamic linked library for TAFC utils |
The following commands enable you to edit remote.cmd.
- SET DRIVER_HOME=%TAFC_HOME%\XMLMSSQL
- SET JBCOBJECTLIST=%JBCOBJECTLIST%;%DRIVER_HOME%\lib
- SET PATH=%PATH;%TAFC_HOME%\bin;%DRIVER_HOME%\bin
- SET JEDI_XMLMSSQL_SQLNCLIPROGID=SQLNCLI11
You can configure the MSSQL Server Direct connect driver using the config-XMLMSSQL executable. This creates the jedi_config driver configuration file at %TAFC_HOME%\config, which stores all the data entered through this executable.
You can configure the server for the database by entering the machine name or IP address of the MSSQL Server.
The first database is considered the default database. You can configure a maximum of ten databases with its own (server and user) credentials.
You can list or change the current settings using the options in Database menu.
You can add or edit the database settings as required using the Set Database option in Database menu.
You can use this option only for the configuration of the default database.
You can configure the user credentials of the first (default) database using the Set DB login user name and Set DB login password options in User menu. If you do not configure the user credentials for other databases, the user credentials of the first database is made available for all the databases.
You can list or change the current settings using the options in User menu.
By default, all the database objects created are stored in dbo schema.
The install.sql script is available at %DRIVER_HOME%\sql. When the path is given, config-XMLMSSQL loads the scripts, invokes sqlcmd at the command prompt and executes the script.
The install.sql script does the following.
- Creates the database according to the specified database names
- Creates the user logins with specified passwords
- Specify the user role as DB owner of the database
- Grants create, insert, update and select permissions to the user
- Creates STUBFILES table for table creation cross reference
- Creates T24LOCKTABLE to store the locks
- Creates ASSEMBLY numsort
- Creates functions like numsort, numcast
- Creates a stored procedure WRITEJOBLIST
- Creates a view for the stubfiles.
The script repeats these steps for all the databases that are configured using Database Settings.
Commands for Multiple Database Access
This section provides examples of commands that can be used with the MSSQL driver and expected output. These commands are mostly built in the Temenos Transact environment, which you can execute with the necessary options when required.
You can use the CREATE-FILE command with a type qualifier (TYPE) to define the file to be created as a table in the MSSQL server database. For example, TYPE=XMLMSSQL.
The above command generates the following tables in the MSSQL server database.
|
Table |
Description |
|---|---|
|
D_EXAMPLE_TABLE |
This table equates to the dictionary section |
|
EXAMPLE_TABLE |
This table equates to the data section. The naming convention shows that the dots in the file name are converted to underscores in table name. |
Both the tables have two columns as listed in the following table.
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
RECID |
Holds the primary key of the table |
|
XMLRECORD |
Holds the table data. |
Generally, the dictionary files are held as NOXMLSCHEMA types (BLOB) as these files are not usually queried.
For each table a cross reference entry is created in the STUBFILES table with the MSSQL server RDBMS database. In addition, a native file stub is also created for each table in the specified file path (in the above example, it is the current directory). The stub files are used to locate and invoke the correct driver for the corresponding table.
Based on the conversion, the stub file information may alternatively be contained within VOC, (which in turn can also be an RDBMS table), ensuring that all the related information is completely contained within the database.
The file is created in the default database, in the dbo schema.
You can create a file in any other database using the DATABASE qualifier. The following table lists the options that can be used in CREATE-FILE.
|
Qualifier |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
TYPE |
XMLMSSQL |
Indicates the type of the file to be created. |
|
DATABASE |
User specified |
Indicates the name of the pre-existing database in which the table needs to be created |
|
TABLE |
User specified |
Indicates the name of the table |
|
READONLY |
YES |
Indicates if the table is to be considered as read-only (applicable only for the data file). |
|
NOXMLSCHEMA |
YES |
Uses BLOB data type instead of XML data type to write the XML data |
|
XSDSCHEMAREG |
YES |
Registers XSD SCHEMA in the database. |
|
XSDSCHEMA |
User Specified |
Uses XSD schema to describe the data layout required for long tag XML format data. |
|
KEY |
VARCHAR[User specified length in integer] or INTEGER |
Indicates the key to alter the data type and length of RECID |
|
ASSOCIATE |
YES |
Indicates if the table has an associated read only table. |
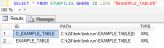
The following example shows a table created in the TSTDB2 database.
The VOC of the table gives the information about the location of the table as follows.
VOC of EXAMPLE.TABLE
VOC of EXAMPLE.TABLE.TSTDB2
Location of EXAMPLE. TABLE in MSSQL Server
The two cross reference table entries are created in the RDBMS STUBFILE table.
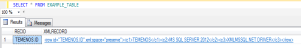
After the table is created, you can add the sample data to the table using standard tools like the command line editor ED or screen editor JED.
You can then view the sample XML data using the MSSQL Server SQL select statement with the XMLRECORD column.
You can use the DELETE-FILE command to delete the file. This command deletes both the DICT and DATA parts of the corresponding table in the database and deletes the reference from the stub.
The MSSQL driver detects the table in any of the database and deletes the table, cross reference and even the stub file entry.
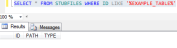
The STUBFILE table update is as follows.
There is no change in the deletion of the file. The driver picks up the name of the database in which the database resides from VOC and deletes it.
The CREATE-VIEW command enables you to create a view of the table such that, the column names can be used within SQL statements to refer the underlying XML. The command will process all the extended dictionary entries related to the file and generates the appropriate view in the MSSQL Server RDBMS database. You need to use the verbose option (-v) to output the generated view to the terminal. This command will be executed against the table on a rebuild of the Temenos Transaction Standard Selection.
If the corresponding file is not the default file in another database, VOC is used to resolve the location of the table.
The CREATE-EXTINDEX command enables you to create indexes in the MSSQL Server RDBMS tables. You need to execute this command manually from the command line, as it is not invoked by any Temenos Transact action.
The MSSQL Server has a limitation, whereby the primary XML indexes can be created only if the key field is less than 128 characters. Temenos Transact creates tables with primary key fields of 255 characters, by default. However, the primary key field must be limited to 128 characters when creating a table. An additional qualifier (KEY) for the CREATE-FILE command is provided.
To limit the primary key field to 128 characters, you need to append the following qualifier to the CREATE-FILE command line.
KEY=VARCHAR[128]
The following table lists the options to be used with the CREATE-EXTINDEX command.
|
Options |
Description |
|---|---|
|
x |
Creates an XML index |
|
v |
Displays the scripts used to create the index |
|
PRIMARY |
Creates only the primary index |
|
PATH |
Creates a secondary XML index on PATH |
|
VALUE |
Creates a secondary XML index on VALUE |
|
PROPERTY |
Creates a secondary XML index on PROPERTY |
|
ALL |
Creates all the primary and secondary XML indexes |
You can use the CREATE-EXTINDEX command to create index on tables of the other databases as well in the similar way.
The DELETE-EXTINDEX command enables you to delete all the indexes created on a table. You can use this command on any table irrespective of the location of their database.
Table Creation Using Long Tag XML
Generally, the XML Schema Definition document (.xsd) is not required for MSSQL Server and XML Schema Definition is not registered, by default. However, you can use the long tag elements as per the Temenos Transact XML Schema Definition (.xsd) document and store the definition within the table. The short tag XML is the default format.
You can invoke the long tag table XML format by specifying the XSDSCHEMA qualifier when creating the table.
The XML Schema Definition (ACCOUNT in this case) must be:
- Generated by the Temenos Transact Standard Selection Rebuild (See XSD Schema Generation User Guide)
- Placed in the MSSQL Server Driver schema directory
By default, the XML Schema Definition is not registered in the MSSQL Server RDBMS Database. To register the XML Schema Definition manually, you can add the additional qualifier XSDSCHEMAREG with the CREATE-FILE command line set to YES. For example, XSDSCHEMAREG=YES.
The following screen capture displays the following.
- A MSSQL Server describe, which shows the table type to be the same as short tag table description
- A select of the XML data shows the Long Tag format
MSSQL allows creation of PRIMARY and SECONDARY XML indexes. The PRIMARY XML index must be created prior to any SECONDARY XML index.
The SECONDARY XML indexes can be created on PROPERTY, VALUE or PATH. The SECONDARY INDEX created with any of these values automatically creates a PRIMARY INDEX, by default. If the keyword ALL is specified, all four indexes are created in one command.
Table Querying
You can use the general jBase Query Language (JQL) queries used to query a J4/JR file, to query the tables as well. The driver converts these queries to the corresponding underlying database query and fetches the data. The translated query is logged in the log file. If the translated query is to be displayed on the standard output, you need to set JEDI_XMLDRIVER_DEBUG_DISPLAY. The following are the different commands involved in querying tables.
The Temenos Transact data is classified into volatile (transactional) and non-volatile (read-only) data. The volatile data is retained in LIVE or default database. The non-volatile data is moved to the second database referred to as non-volatile DB.
You can create read-only tables in any of the configured database. However, you cannot do the following.
- Create a DICT file for the read-only table
- Write, clear or delete a record from the READ-ONLY table. It results in a coredump and generates a log
The Temenos Transact table will have an associated RO table if the LIVE file contains an ASSOCIATE flag in VOC. This RO table can reside in any of the configured databases.
The LIST-EXTINDEX command on the LIVE table gives the details about the indexes created on the associate RO table as well.
If the LIVE database has an associated RO table in non-volatile DB, the driver queries both the tables and displays the data.
The RO table can be of any name. However, the RO file created should be <“live” file$RO>. A synonym has to be created in the LIVE database as <RO table name> for the RO table.
The user of the first database should have the permission to access and run the scripts on the second database.
When a query is executed on the LIVE file, the records are displayed from both the LIVE file and associated file avoiding the duplicates, by default. If you want to change the default functionality, you need to set the JEDI_XMLDRIVER_ASSOCIATE_FILE variable to any of the following values, as required.
|
Value |
Functionality |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Disables the redirection and query to the ASSOCIATE table |
|
2 |
Disables query for ASSOCIATE table, but redirection is active |
|
4 |
Disables PDATE in the query, but redirection and ASSOCIATE table query with UNION will be active |
The following screen captures display querying with search criteria on a left and right justified field, respectively.
Transaction in Multiple Databases
When a WRITE or UPDATE action is performed within the transaction boundary (between TRANSTART and TRANSEND), it is termed a transaction. When a transaction involves files from multiple databases, the transaction starts in WRITE. The transaction can also read a file from one database and write to another file from a different database.
Updating or writing data to the files of multiple databases results in a coredump.
Mirrored Configuration Failover
The MSSQL Server Direct Connect Driver now supports the Fail over condition on Mirrored MSSQL Server Database configuration by specifying the Failover Partner server name in an environment variable.
This change allows the driver to be specified with an optional FailoverPartner connection parameter when the SQL Server database(s) are operating in mirror mode (High Availability or High Protection mode) with automatic failover. This configuration will have both the principal and mirror databases. During failover, the mirror will become the principal database.
You can optionally specify the FailoverPartner connection parameter to the driver using the following environment variable.
SET JEDI_XMLMSSQL_FAILOVERPARTNER=<server\instance name>
When the primary server (defined as Server Name in jedi_config) and its mirrored partner (specified in the above environment variable) are available and if a failover condition occurs, the driver will automatically connect to the appropriate principal server.
The driver does not handle the error conditions, which occur during failover and reconnect automatically. In this scenario, Temenos Transact exits the connection from the primary server and establish a new connection with the mirrored server. The driver will connect to the appropriate principal server only in the latter case.
Driver Environment Variables
You need to configure the following environment variables to be used with the MSSQL Server Direct Connect Driver.
Internationalisation
- JBASE_I18N=1 (Mandatory)
- JBASE_CODEPAGE=utf8
- JBASE_LOCALE=en_US
- JBASE_TIMEZONE=Europe/London
MSSQL Server (Mandatory)
- JEDI_XMLMSSQL_SQLNCLIPROGID=SQLNCLI10 (for MS SQL SERVER 2008)
- JEDI_XMLMSSQL_SQLNCLIPROGID=SQLNCLI11 (for MS SQL SERVER 2012)
Optional
The following table lists the optional variables and their functionality.
|
Command |
Functionality |
|---|---|
|
JEDI_XMLDRIVER_TRACE=1 |
Traces all driver functions |
|
JEDI_XMLDRIVER_DEBUG_DISPLAY=1 |
Traces only query translations |
|
JEDI_XMLDRIVER_NO_SPACE_PRESERVE=1 |
Indicates that the white space is not preserved in xml Trace |
|
JEDI_XMLDRIVER_PREFETCH_ROWS = n |
Indicates the number of rows to be pre-fetched in each fetch. The default value is 500. |
|
JEDI_XMLDRIVER_ENABLE_DB_SORT=1 |
Enables the DB sort instead of JQL Sort |
|
JEDI_XMLDRIVER_DISABLE_RECID_NUMSORT=1 |
Ignores the data type of the RECID while sorting on RECID |
|
JEDI_XMLDRIVER_ENABLE_EDICT_TYPE=1 |
Enables the EDICT data type detection |
|
JEDI_XMLDRIVER_DISABLE_DATABASE_LOCKS=1 |
Disables the DB row locks |
Add Bookmark
save your best linksView Bookmarks
Visit your best links BACK
BACK
In this topic
Are you sure you want to log-off?