| Bookmark Name | Actions |
|---|
Introduction to CRS Client Identification
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) defined the following in the Standard for Automatic Exchange of Information in Tax Matters:
- The Model Competent Authority Agreement (CAA) serves as a template for intergovernmental agreements
- The Common Reporting Standard (CRS) displays the reporting and due diligence standard that underpins the automatic exchange of information.
Model Competent Authority Agreement (CAA)
The Model CAA displays the following clauses that aim at effective information exchange along with the type of information for exchange, along with the time and manner of such exchanges.
- Due diligence
- Domestic reporting
- Data confidentiality
- Infrastructure
For uniformity on agreements, the OECD has published model agreements, such as bilateral and multilateral. They also have a model nonreciprocal agreement for a jurisdiction where no income tax regime exists and the contracting state does not wish to receive information on its residents’ banking activities in the partner country.
Common Reporting Standard (CRS)
The CRS is an information standard that facilitates automatic exchange of information (AEoI), developed in the context of the OECD and is effective since 01 Jan 2016. The OECD standard is a step change in the way in which jurisdictions share tax information to combat tax evasion.
The OECD acknowledges that many jurisdictions exchange information automatically, often on certain common types of income, most notably within the EU. However the standard is intended to be global in scope and to focus on a universal set of information relating to financial accounts, drawing heavily on the intergovernmental approach adopted under FATCA.
Thus, CRS is a global standard, which contains due diligence and reporting requirements that are the foundation of automatic information exchange to reduce inconsistencies and help minimise compliance cost to the financial institutions, particularly institutions operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Thus, under CRS, FIs have to report on the account holder’s information who are tax resident in other participating jurisdictions Participating jurisdictions enact rules in domestic laws that are consistent with the provisions of the CRS.
CRS captures all relevant taxpayers with a broad scope across four main areas consistent with FATCA’s intergovernmental approach.
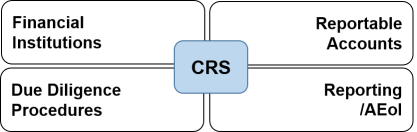
The institutions listed below must report to CRS
- Banks
- Custodians
- Brokers
- Collective investment vehicles,
- Trusts and certain insurance companies
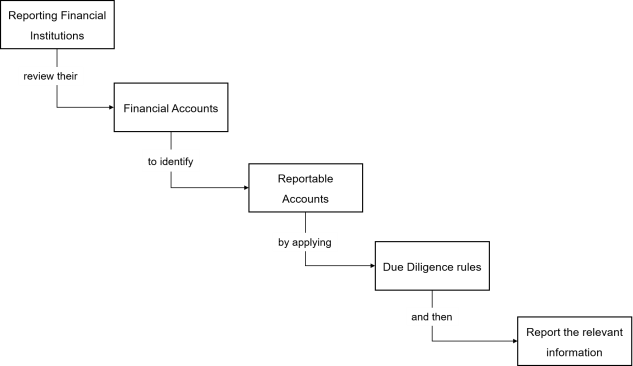
Identifying the reporting Financial Institutions
The following diagram enables the user to understand the process flow in identifying a reporting financial institution.

This section includes accounts held by:
- Individuals
- Entities (includes trusts and foundations), and the requirement to look through passive entities to provide information on reportable controlling persons.
It also includes reportable income such as:
- Investment income (interest, dividends, income from certain insurance contracts, annuities and similar sources),
- Account Balances
- Sales proceeds from financial assets that in turn raises income.
Review the Financial Accounts to identify reportable accounts.
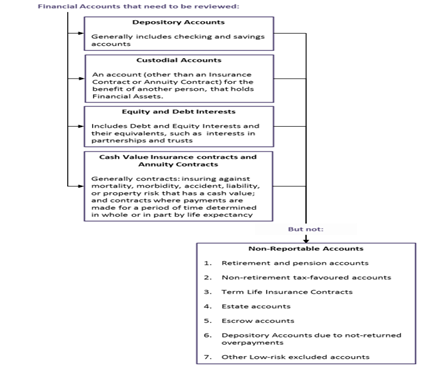
To identify reportable accounts and obtain accurate, required information, financial institutions must follow a common standard with robust due diligence procedures. These procedures distinguish between individual accounts and entity accounts and between pre-existing and new accounts:
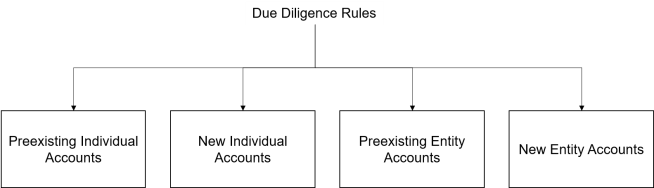
Financial institutions are required to review pre-existing individual accounts without applying of any de minimis threshold, though different procedures apply to higher value accounts and lower value accounts.
- Lower Value Accounts—a country can allow a financial institution to perform an indicia search or to rely on a permanent residence address test. Self-certification (documentary evidence) is needed in case of conflicting indicia. If no such certification can be found, reporting can be carried out to all reportable countries for which indicia is found.
- Higher Value Accounts—enhanced due diligence procedures apply, including a paper record search and a reason to know test for the relationship manager enquiry. The relationship manager of a high value account is the officer or employee of the financial institution, with direct contact and primary responsibility for managing the account.
The CRS contemplates self-certification (and the confirmation of its reasonableness) without de minimis threshold.
Financial institutions determine whether the entity is,
- A reportable person, which can be verified on the basis of information available (AML/KYC procedures), or, through self-certification.
- A passive NFE and must confirm the residency of controlling persons. Where possible, this can be achieved through available information, but requires obtaining a self-certification from an account holder or controlling person of a passive NFE where applicable.
If the domestic country allows and the individual financial institution elects to apply it, the pre-existing entity accounts below 250,000 US dollars (or local currency equivalent) are not subject to review until such time as the account exceeds US$250,000 at the end of the subsequent year.
Financial institutions must follow the same determination similar to pre-existing accounts. However, as it is easier to obtain self-certifications for new accounts as part of account opening process, the US$250,000 (or local currency equivalent) threshold does not apply, and the residency of controlling persons of passive NFEs must be determined on the basis of self-certifications.
CRS Process Workflow
The CRS process workflow is shown below.
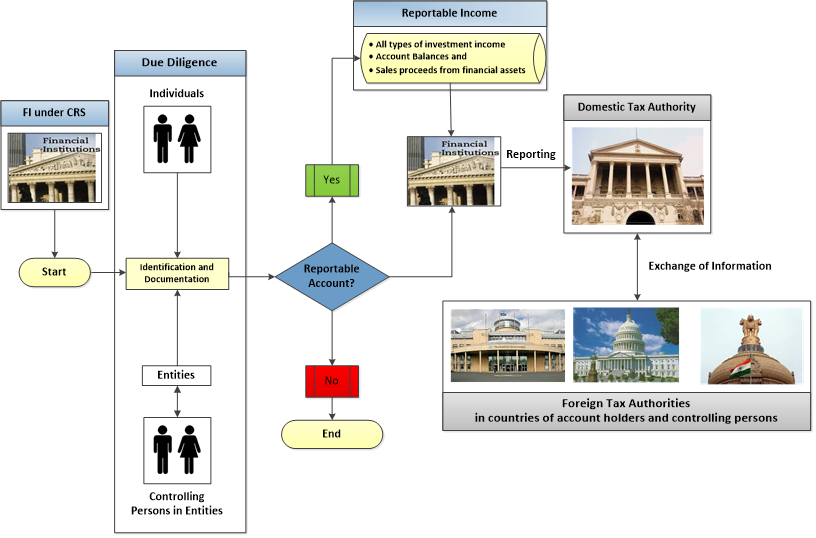
The CRS Solution in Temenos Transact scales through the below processes:
- Balance Aggregation process for the pre-existing and for new accounts.
- Classification of the pre-existing and new accounts into Individuals and Entities.
- Due-Diligence process for the pre-existing and new accounts.
- Process to work out the indicia’s as part of the due-diligence process.
- Recording of the mandatory information for the new accounts.
- Reporting of both pre-existing and new accounts.
Configuring CRS Client Identification
In Temenos Transact, the CRS functionality is offered under the following module licenses:
- CD module licensing covering Client Identification and Due Diligence
- CE module licensing covering the AEoI Reporting Solution.
The CD module licensing supports banks to identify all customers reportable under the CRS Regulation by due diligence process.
- The year during which the regulation becomes effective.
- Ability to identify whether the customer having a tax residence in a country under participating jurisdiction and becomes reportable, with a facility for automatic update at regular intervals in case of changes in the jurisdictions.
- Initial Balance Aggregation process for all customers and subsequent aggregations only for CRS customers.
- Classification of customers into individuals & entity segregating balances into high and low values.
- Due Diligence process based on the Indicia given by the regulators and capturing of mandatory information for new accounts.
- Holding of clients’ information linked to the codes as prescribed by schema.
For customers identified as above, the CE module supports generation of XML reports towards CRS compliance through automatic exchange of information.
- Reporting is controlled based on high level parameter set up governing CRS Reporting.
- Base file is created to store all the required information for Reporting. Special feature to identify and report Dormant accounts separately
- Provision to amend the base file for corrections, if any
- Generation of XML Report.
This parameter table enables the user to define indicia calculation rules for CRS and define the mapping of fields for the creation of the CRS.CUST.SUPP.INFO for corporate customers.
The user can define the indicia mapping rules for both corporate and/or individual customers as shown in the below screenshot.
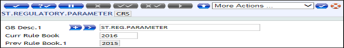
ST. REGULATORY.PARAMETER
Temenos Transact supports a generic regulatory parameter to track all regulatory releases. This performs checks before releasing the functionality for the existing Regulations licensed from Temenos Transact.
Following information are captured in the table:
The ID is a valid Regulatory ID. In this context, it is CRS.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| GB Desc.1 | Provides the description for the chosen regulation. |
| Curr Rule Book | Ranges from 1950–2049, anything before and after the specified year displays an error. |
| Prev Rule Book | Displays the previous releases of regulation. Before the value in the Curr Rule Book field is overwritten to reflect the latest release, the system automatically updates the current value before modification to the value in the Prev Rule Book field. |
To view the setup for ST.REGULATORY.PARAMETER, go to Admin Menu > Compliance and Regulatory Administration > CRS > Regulatory Details > Regulatory Parameter.
CRS.PARAMETER
This parameter is used for recording the details such as effective date, participating jurisdiction, reporting currency and setting up default conditions required for reporting purposes. The table holds these definitions company wise
Any country included or withdrawn from the regulatory process will lead to the automatic calculation of the Indicia and the reportable jurisdiction based on the option provided here.
The CRS.PARAMETER table displays the regulatory details at company level. The ID is a valid Company code.
The below screenshot displays a sample view of the Regulatory Specific High Level Parameter:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Partng Juridict | Lists the participating countries for CRS Regulation. |
| Telephone Code | Indicates the telephone code assigned to the value displayed in the Partng Juridict field. This is an associate field for Partng Juridict field and displays the telephone code based on the Country. Valid countries are made available in the Temenos TransactCOUNTRY table. |
| Indicia Calc Rtn | Enables provision to hold the ID to the routine that calculates the Indicia Status. This field is mandatory to calculate the Indicia strength. NOTE: Clients have the option to use their own routines or use an API supported by Temenos Transact, CRS.GET.INDICIA. |
| Close.Rel.Bal.Type | Decides whether the previous day customer balances should be calculated when the CRS Status field is changed to INACTIVE. Allowed Values are: PREVIOUS.MONTH and PREVIOUS.DAY . |
| Reporting CCY | Specifies the currency used for Balance Aggregation process. |
| Auto Status Update | Displays whether there has been an automatic change in the status. Accepted values are yes and No. If there is a change in Indicia, the system updates the status of this field for CRS Reporting automatically when set as “yes”. |
| SC Grace Days | Specifies the maximum number of days for submission of Self-Certification documents by clients. Also used to calculate the date displayed in the Cut Off Date field in the Req Date field specified in CRS.CUST.SUPP.INFO. |
| Account Type | Lists out the different type of accounts for classification of existing accounts. |
| Account Sub Type | Specifies further classification of account type to HIGH or LOW based on the balance aggregation. |
| Reporting Date | Specifies the reporting date of the account types and it can be set to a current date or a future date. |
| Initial Aggr Built | Identifies whether the initial aggregation process for all the existing customers is run. The system updates this field as 'YES', once the initial aggregation is completed. Once this field is set, subsequent aggregation process happens only for CRS reportable customers’ i.e. for customer having CRS.CUST.SUPP.INFO records. |
| Bal Amt Aggr From | Holds the lower range of the aggregation amount for the corresponding account type for account classification of Pre-Existing accounts. |
| Bal Amt Aggr To | Holds the upper range of the aggregation amount for the corresponding account type for account classification. |
| Due Diligence Date | Specifies the due diligence dates for Pre-Existing Individual Low, Pre-Existing Individual High and Pre-Existing Entity High accounts. |
| Country Rule | Displays whether the country is INDIVIDUAL (one XML file per customer) or BULK (one consolidated XML output). This field is set to BULK in order to trigger the Merge.Rtn field. |
| EB.Transfm.Key | Applies the changes in local XSLT transformation or schema changes. Default EB.TRANSFORM rule applied is 'CRS.REPORT.BASE.XSLT', if this field is left blank. Data in the first multi value position is for XSLT transformation of individual customer specific XMLs. And the second multi-value is used for merged XML output. The below screenshot displays the sample setup for Luxembourg |
| Dorm Ident App | Defines the application for identifying dormancy. Allows any Temenos Transact application. |
| Dorm Ident Field | Defines the field of the application from where dormancy is identified |
| Dorm Ident Operand | Accepts the operands 'EQ' 'NE'. |
| Dorm Ident Value | Holds the value of Dorm Ident.Field above. |
| EIN | Holds the identification number used by the sending tax administration to identify the Entity Account Holder. |
Go to Admin Menu > Compliance and Regulatory Administration > CRS > Parameter Details > CRS > Parameter Input, update the CRS Parameter for the company operating in with the details as below:
- The participating jurisdiction is set as “GB”.
- The telephone code is indicated as “+11”.
- Indicia Routine to be used is set as “CRS.GET.INDICIA”.
- Reporting currency to be USD - Auto status update as yes – Close Relationship Balance type to be Previous day.
- For Pre-existing Entity, the sub types are high and low. The Balance amount aggregation up to 249,999 is low and from 250,000 is Account sub type high.
- For Pre-existing Individual, the sub types are high and low. The Balance amount aggregation up to 999,999 is low and from 1,000,000 is Account sub type high.
- For New entity & New individual- by default all accounts are reportable.
- Reporting date and due diligence date are to be fed for all sub types except sub type Entity – Low.
Below screenshot displays the Parameter table.
CRS Workflow
The CRS workflow is as follows:
- Set up CRS.CLIENT.TYPE
- Set up ST.REGULATORY.PARAMETER
- Set upthe RT.REGULATORY.RULES table for field and indicia mapping
- Set up CRS.PARAMETER
- Set up BNK/ST.UPDATE.INDICIA – batch record
- Create a CUSTOMER record which satisfies the indicia for CRS.
- Run COB
- The CRS.CUSTOMER.SUPPLEMENTARY.INFO records are created.
The CRS.CUST.SUPP.INFO record is automatically created for corporate customers after the above steps are successfully completed. New features function correctly only if the configuration steps are completed successfully. To know more, refer to Due Diligence.
Illustrating Model Parameters
Parameters configured in Model Bank are detailed below:
| S.No. | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ST.REGULATORY.PARAMETER
|
|
| 2. | CRS.PARAMETER
|
|
| 3. | ST.AGGREGATION.PARAM
|
|
| 4. | ST.AGGREGATE.BALANCES
|
|
| 5. | CUST.REASONABLENESS.CHECK.PARAMETER
|
This application allows the user to define the fields that are used for reasonableness check. The ID of the application is CRS.
|
Illustrating Model Products
Model Products are not applicable for this module.
Add Bookmark
save your best linksView Bookmarks
Visit your best links BACK
BACK
In this topic
Are you sure you want to log-off?